Appendix: Monitoring Template
Risk: Foundation models increase the number of people with the potential capability to create a weapon and decrease team sizes and coordination costs required, thus increasing the chance that a domestic malicious actor creates and uses one.
In this risk scenario the availability of foundation models increases access for wider portions of the population, per haps through the use of an LLM that can walk an individual through the steps required to create a weapon. This risk is distinct from the risk posed by scientifically sophisticated actors creating new weapons with increased potency. The discovery of a new weapon could also involve a model specifically developed to handle specialized knowledge (such as a biological design tool), which requires special ized expertise to use.
Collecting Evidence:
To create a weapon, an individual may need both specialized knowledge and appropriate materials. As model capabilities change, evaluators would need to gather and maintain information about the changing knowledge and material needs of actors seeking to create specific categories of weapons, which would require expertise in both science and machine learning. Evaluators may need to keep multiple risk profiles for different risks. Specific risk indicators might include, along with progressively less re strictive values of those indicators:
- What level of specialized knowledge is required to use the foundation model to create the de sired weapon
- Specialized doctoral degree or higher
- Specialized master’s degree
- Specialized bachelor’s degree or hobbyist “home scientists”
- Average adult
- Where can an individual get the materials to make the desired weapon?
- Specialty supplier, heavy regulation such as licensed sellers and buyers
- Specialty supplier, light regulation such as pur chase tracking
- Specialty supplier, no legal restrictions but typically has administrative barriers
- Local store or Internet search
To gather this information, evaluators could begin by red-teaming open and closed cutting-edge models. Subject-matter experts would consider the additional assistance that the model provides in creation of a weapon. They would also consider the equipment required, including whether the model finds methods to use more easily available materials than might be purchased through a laboratory supplier. Other methods might be used, as determined by the subject-matter experts.
Evaluating Evidence and Acting on Evaluations:
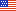
The grid below shows a set of potential mitigation options which are dependent on the risk indicators. The government agency responsible for managing the risk scenario would choose from potential mitigation options, which could involve technical restrictions or a variety of other non-model-oriented actions designed to reduce risk. Developing such a ma trix would require an understanding of different legal and regulatory authorities and may involve collaboration between agencies. In the example decision matrix below, the value in each entry shows possible mitigation options, which the agency may or may not decide to recommend.
Mitigation Options:
- Do nothing
- Restrict open model weights & access to closed models, for specific classes of models
- Restrict access to specific materials
- Security controls on API-based fine-tuning of closed models using specific types of data (biological, chemical, etc.)
Who is enabled by AI to create a weapon? | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Where can an individual get the materials to make a weapon? | Average person | Specialized bachelor’s degree/ hobbyist | Specialized master’s degree | Specialized doctoral degree | |
| Local store/ internet search | 1 or 2 or 3 | 1 or 2 or 3 | 1 or 2 or 3 | 2 or 3 | |
| Specialty supplier, no legal restrictions | 1 or 2 or 3 | 1 or 2 or 3 | 1 or 2 | 2 | |
| Specialty supplier, light legal burden | 1 or 2 or 3 | 1 or 2 or 3 | 1 or 2 | 0 | |
| Specialty supplier, heavily regulated | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
Example: If an individual with a specialized master’s degree can use an LLM to make a weapon with materials from a specialty supplier with no legal burden, then the government should consider either (1) restricting access to specific classes of models/weights or (2) restricting access to specific materials.